Athena OS Core Image
Athena OS container brings you to live a funny hacking experience in a containerized environment:
- Select your favourite InfoSec role between Bug Bounty Hunter, Red Teamer, OSINT Specialist and much more
- Play Hack The Box machines for improving your skills
- Explore more than 2800+ hacking tools retrievable by Arch Linux and BlackArch repositories
- Make your Capture The Flag or ethical hacking activity efficient
Click Docker icon above to explore Athena OS Docker containers!
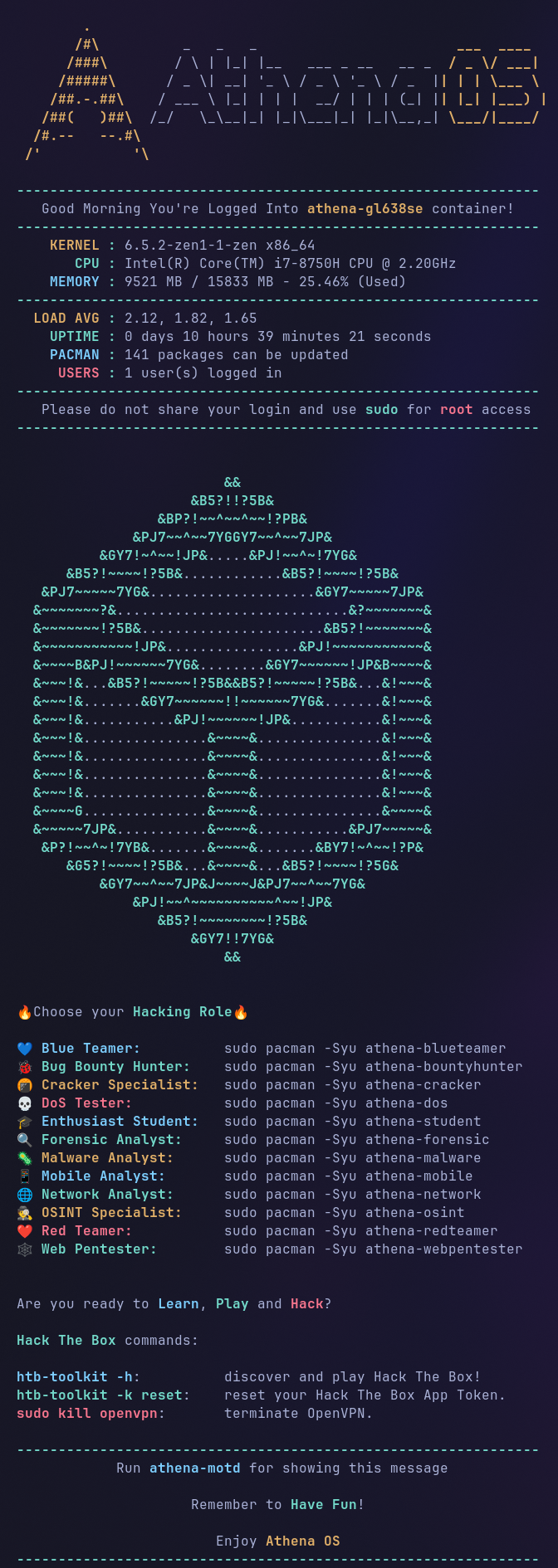
Athena OS container has been developed in order to be run also by podman. The choice to use podman comes from its advantages over docker, one of most important: security.
According to your preference, install docker and docker-compose packages or podman package for your Linux environment.
In case you are using podman, edit /etc/containers/registries.conf and add:
[registries.search]registries = ['docker.io']in order to allow podman to search for images in Docker Hub.
Hack The Box API Token
Section titled “Hack The Box API Token”Athena OS container allows you to learn and play on Hack The Box platform. It is possible to access to Hack The Box by using your App Token. Retrieve your App Token from the Hack The Box website in your Profile Settings.
Docker
Section titled “Docker”Store your App Token in a file called htb-api-file in your current directory, save and close it.
You can run the container by docker-compose (recommended) or docker run.
docker-compose
Section titled “docker-compose”The docker-compose.yml file should have the following content:
version: '3.4'
services: athena: image: athenaos/core cap_add: - net_admin devices: - /dev/net/tun sysctls: - net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=0 secrets: - source: htb-api tmpfs: - /run - /tmp restart: unless-stopped
secrets: htb-api: file: ./htb-api-fileand the htb-api-file must be in the same directory, otherwise you can change its path in docker-compose.yml.
Run the container by:
sudo docker-compose run athenadocker run
Section titled “docker run”docker run -ti \ --name athena \ --volume ./htb-api-file:/run/secrets/htb-api:ro \ --cap-add NET_ADMIN \ --device /dev/net/tun \ --sysctl net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=0 \ --restart unless-stopped \ docker.io/athenaos/core:latestor
docker run -ti --name athena --volume ./htb-api-file:/run/secrets/htb-api:ro --cap-add NET_ADMIN --device /dev/net/tun --sysctl net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=0 --restart unless-stopped docker.io/athenaos/core:latestIn case you exit the container and need to re-enter, run:
docker exec --user athena -ti athena /bin/zshIn case the container is not running, run:
docker start athenaFor stopping the container, run:
docker stop athenaFor deleting the container, run:
docker container rm athenaPodman
Section titled “Podman”Store your App Token in a file called htb-api-file, save and close it, and then run:
podman secret create htb-api htb-api-fileIn this manner, podman will store securely your API key. Now, you can delete the htb-api-file by rm -rf htb-api-file.
You can run the container by podman run.
podman run
Section titled “podman run”podman run -ti \ --name athena \ --secret htb-api \ --cap-add NET_RAW \ --cap-add NET_ADMIN \ --device /dev/net/tun \ --restart unless-stopped \ docker.io/athenaos/core:latestor
podman run -ti --name athena --secret htb-api --cap-add NET_RAW --cap-add NET_ADMIN --device /dev/net/tun --restart unless-stopped docker.io/athenaos/core:latestPodman will automatically replicate /etc/hosts and /etc/hostname files of your host. For preventing this, add --no-hosts argument to the podman run command above.
In case you exit the container and need to re-enter, run:
podman exec --user athena -ti athena /bin/zshIn case the container is not running, run:
podman start athenaFor stopping the container, run:
podman stop athenaFor deleting the container, run:
podman container rm athenaDefault Credentials
Section titled “Default Credentials”athena:athenaParameters
Section titled “Parameters”Container images are configured using parameters passed at runtime (such as those above). These parameters are separated by a colon and indicate <external>:<internal> respectively. For example, -p 8080:80 would expose port 80 from inside the container to be accessible from the host’s IP on port 8080 outside the container.
| Parameter | Function |
|---|---|
| —secret htb-api | usage of App Token on the container |
| —cap-add=NET_RAW | needed for running ping command |
| —cap-add NET_ADMIN | needed for running OpenVPN |
| —device /dev/net/tun | needed for creating tun interface used by OpenVPN |
Updating Info
Section titled “Updating Info”Below are the instructions for updating containers:
Via Podman Run
Section titled “Via Podman Run”- Update the image:
podman pull docker.io/athenaos/core:latest - Stop the running container:
podman stop athena - Delete the container:
podman rm athena - Recreate a new container with the same podman run parameters as instructed above (if mapped correctly to a host folder, your
/configfolder and settings will be preserved) - You can also remove the old dangling images:
podman image prune
Building locally
Section titled “Building locally”If you want to make local modifications to these images for development purposes or just to customize the logic:
git clone https://github.com/Athena-OS/athena-core-docker.gitcd athena-core-dockerdocker build \ --no-cache \ --network host \ --pull \ -t docker.io/athenaos/core:latest .For pushing to Docker Hub, first login to it:
docker loginand then:
docker push athenaos/core:latestThe ARM variants can be built on x86_64 hardware using multiarch/qemu-user-static
docker run --rm --privileged multiarch/qemu-user-static:register --resetOnce registered you can define the dockerfile to use with -f Dockerfile.aarch64. This method has not been tested yet.
